Modern Dental Implant Techniques: How Technology Improves Accuracy

Modern Dental Implant Techniques: How Technology Improves Accuracy
Dental implant procedures have evolved significantly over the past decades. Advances in technology have transformed how implant treatments are planned and executed, improving accuracy, predictability, and patient outcomes.
This educational article explores modern dental implant techniques and explains how technology improves accuracy throughout the implant process. Rather than detailing surgical instructions, this guide focuses on planning methods, digital tools, and technical principles used in contemporary implant dentistry.
Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and does not provide medical or dental advice. Dental implant techniques and outcomes vary based on individual needs and professional judgment.
The Evolution of Dental Implant Techniques
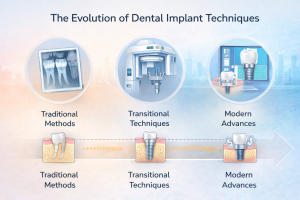
Traditional dental implant placement relied heavily on clinical experience and two-dimensional imaging. While effective, these methods offered limited visualization of bone anatomy and surrounding structures.
Modern implant dentistry integrates digital technology to enhance precision, reduce uncertainty, and support consistent outcomes across a wide range of cases.
Why Accuracy Matters in Dental Implant Procedures
Accurate implant placement is essential for long-term stability, function, and aesthetics. Proper positioning affects how forces are distributed, how restorations fit, and how surrounding tissues respond over time.
Improved accuracy may contribute to:
- Better implant stability
- Optimized bite alignment
- Reduced risk of complications
- More predictable restorative outcomes
Digital Imaging and 3D Diagnostics
One of the most significant advancements in modern dental implant techniques is the use of three-dimensional imaging.
CBCT Imaging in Implant Planning
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) allows dental professionals to view bone structures, nerve pathways, and sinus anatomy in three dimensions.
This level of visualization supports informed planning decisions and helps identify anatomical considerations before implant placement.
Virtual Treatment Planning
Digital planning software enables practitioners to simulate implant placement in a virtual environment before any clinical procedure takes place.
Prosthetically Driven Planning
Modern planning often begins with the desired restorative outcome. Implants are positioned based on functional and aesthetic goals rather than bone availability alone.
This approach aligns surgical planning with restorative needs, improving overall treatment accuracy.
Digital Impressions and Scanning Technology
Intraoral scanners capture detailed digital impressions of the teeth and gums. These scans replace traditional impression materials and support precise restorative design.
Digital impressions contribute to improved fit, reduced adjustments, and streamlined communication between dental professionals and laboratories.
Surgical Guides and Guided Implant Placement
Surgical guides are custom-made devices designed to assist with implant positioning based on digital planning.
How Surgical Guides Improve Accuracy
Guided implant placement uses pre-planned pathways to support precise angulation and depth control.
While not used in every case, guided techniques may enhance consistency in suitable scenarios.
Technology and Risk Management
Modern dental implant techniques emphasize risk assessment and prevention. Digital tools help identify potential challenges before treatment begins.
By anticipating anatomical limitations, dental professionals can adjust treatment plans to support safer and more predictable outcomes.
Limitations of Technology-Based Techniques
While technology improves accuracy, it does not replace clinical judgment. Digital tools must be interpreted and applied by trained professionals.
Successful implant outcomes depend on combining technology with experience, skill, and individualized care.
Guided vs Freehand Dental Implant Techniques
Modern dental implant placement may be performed using either guided or freehand techniques. Each approach has distinct characteristics and may be selected based on clinical needs, case complexity, and practitioner preference.
Guided Implant Placement Overview
Guided implant placement uses digitally designed surgical guides created from three-dimensional imaging and virtual planning. These guides help transfer the digital plan to the clinical setting.
Potential advantages of guided techniques include:
- Improved positional accuracy
- Enhanced alignment with restorative goals
- Consistent implant angulation and depth
Guided methods are commonly used in cases where precision is especially important.
Freehand Implant Placement Overview
Freehand placement relies on clinical judgment, experience, and real-time assessment during the procedure. Many experienced practitioners successfully use freehand techniques.
While freehand methods may offer flexibility, they depend heavily on practitioner skill and familiarity with anatomy.
Flapless vs Traditional Surgical Approaches
Another distinction in modern dental implant techniques involves how soft tissues are managed during placement.
Flapless Implant Techniques
Flapless techniques involve placing implants without making large incisions in the gum tissue. This approach is typically considered when sufficient bone and favorable anatomy are present.
Potential considerations include:
- Reduced tissue disruption
- Shorter early recovery periods
- Limited visibility for certain cases
Traditional Flap Techniques
Traditional approaches involve reflecting the gum tissue to visualize the underlying bone. This method allows direct assessment of bone contours and anatomical landmarks.
Both approaches may be appropriate depending on individual case requirements.
Digital Workflow Integration
Modern dental implant techniques often integrate digital workflows that connect diagnostics, planning, surgery, and restoration.
From Planning to Restoration
Digital workflows allow treatment data to be shared across stages of care. Imaging, digital impressions, and planning software work together to support accuracy and efficiency.
This integration can improve communication between dental professionals and laboratories.
The Role of CAD/CAM Technology
Computer-Aided Design and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAD/CAM) technology supports the fabrication of implant restorations.
CAD/CAM systems enable precise design of crowns and prosthetics that align with digitally planned implant positions.
This level of coordination supports improved fit and function.
Accuracy vs Clinical Experience
While technology improves accuracy, clinical experience remains a critical factor in successful implant outcomes.
Digital tools support decision-making but do not replace professional judgment.
Experienced practitioners use technology to enhance—not replace—their understanding of anatomy and biomechanics.
When Advanced Techniques May Not Be Necessary
Not every dental implant case requires advanced digital techniques. Straightforward cases with adequate bone and favorable anatomy may be successfully managed using conventional methods.
Technology is best applied selectively, based on patient-specific needs rather than as a one-size-fits-all solution.
Balancing Innovation and Practical Application
Modern dental implant techniques represent a balance between innovation and practical clinical application.
Appropriate use of technology supports precision and predictability while maintaining individualized patient care.
Frequently Asked Questions About Modern Dental Implant Techniques
Do modern dental implant techniques improve success rates?
Modern dental implant techniques are designed to improve planning accuracy and predictability. While success depends on many factors, advanced imaging and digital planning may help reduce positioning-related complications.
Is guided implant surgery better than traditional methods?
Guided implant surgery may offer increased precision in certain cases, but traditional freehand techniques remain effective when performed by experienced professionals. The choice depends on individual clinical needs.
Does technology reduce the need for surgical experience?
Technology supports decision-making but does not replace clinical expertise. Successful outcomes rely on combining digital tools with professional judgment and experience.
Are modern techniques used for all implant cases?
No. Some straightforward cases may not require advanced digital workflows. Technology is applied selectively based on case complexity and treatment goals.
Key Advantages of Technology-Assisted Implant Placement
Modern dental implant techniques offer several potential advantages when used appropriately:
- Enhanced visualization of anatomical structures
- Improved alignment with restorative goals
- Greater consistency in implant positioning
- Streamlined collaboration between clinical and laboratory teams
These benefits contribute to predictable workflows and patient-centered treatment planning.
Limitations and Considerations
Despite their advantages, technology-based implant techniques have limitations. Equipment costs, learning curves, and case selection play important roles in determining when these tools are appropriate.
Additionally, digital plans must be carefully translated into clinical execution to avoid discrepancies.
How Patients May Benefit From Modern Implant Techniques
From a patient perspective, modern dental implant techniques may support clearer communication, more predictable timelines, and well-coordinated care.
Patients may also appreciate visual explanations made possible through digital imaging and virtual planning.
The Future of Dental Implant Technology
Dental implant technology continues to evolve, with ongoing advancements in imaging, materials, and software integration.
Future developments may further enhance accuracy, efficiency, and personalization of implant treatment while maintaining a focus on safety and long-term outcomes.
Summary: Technology and Accuracy in Implant Dentistry
Modern dental implant techniques emphasize precision through advanced imaging, digital planning, and guided workflows. When applied thoughtfully, these tools support accurate implant placement and coordinated restorative outcomes.
However, technology works best when combined with professional expertise and individualized treatment planning.
Final Thoughts
Understanding how technology improves accuracy in dental implant procedures helps patients appreciate the planning and care involved in modern treatment.
While techniques continue to advance, successful dental implant outcomes remain rooted in comprehensive evaluation, skilled execution, and long-term follow-up.
Final Disclaimer: This article is intended for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical or dental advice. Treatment methods and outcomes vary. Patients should consult a licensed dental professional for personalized guidance.


Leave a Comment
Your comment will be published after it has been approved. Please send comments that do not contain slang words.